Spevigo (spesolimab) has a conditional marketing authorisation for the treatment of generalised pustular psoriasis (GPP) flares in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age as monotherapy
▼This medicinal product is subject to additional monitoring. * Additional efficacy and safety data are being collected.
Click here for prescribing information.
SPEVIGO®▼ (spesolimab) was evaluated for the treatment of GPP flares1,2
EffisayilTM 1 was a Phase II, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of SPEVIGO® in patients with GPP presenting with a flare1,2

Inclusion criteria were regardless of IL-36RN mutation status.
Patients aged 18 to 75 years with GPP, as defined by ERASPEN:
Primary, sterile, macroscopically visible pustules on non-acral skin (excluding cases in which pustulation is restricted to psoriatic plaques)
With or without systemic inflammation, with or without plaque psoriasis; can be either a relapsing condition (>1 episode) or a persistent condition (>3 months)
Evidence (or previous evidence) of systemic symptoms:
Fever
Asthenia
Myalgia
Elevated CRP level
Leucocytosis with peripheral blood neutrophilia (above ULN)
IL-36RN=interleukin-36 receptor antagonist; ERASPEN=European Rare and Severe Psoriasis Expert Network; GPP=Generalised Pustular Psoriasis; ULN=upper limit of normal; CRP=C-reactive protein.
Patients were excluded if they presented with:
SAPHO syndrome
Plaque psoriasis without pustules or with pustules restricted to psoriatic plaques
Drug-triggered AGEP
Immediate, life-threatening GPP flare or required intensive care treatment
Dose escalation of their maintenance treatment with ciclosporin, retinoids or methotrexate within 2 weeks prior to randomisation
Treatment with any drug, including biologics and systemic drugs, considered likely to interfere with the safe conduct of the study or any prior exposure to an IL-36R inhibitor
| Patients were required to discontinue systemic and topical therapy for GPP prior to randomisation* | |
|---|---|
| Duration of washout period | Medications or class of medications |
| 2 months | Adalimumab, alemtuzumab, briakinumab, brodalumab, efalizumab, guselkumab, infliximab, ixekizumab, natalizumab, risankizumab, rituximab, secukinumab, tildrakizumab, ustekinumab, visilizumab, investigational products for psoriasis (non biologics) |
| 6 weeks | Etanercept |
| 30 days | Systemic immunomodulatory treatments (e.g. corticosteroids†, cyclophosphamide), tofacitinib, apremilast; other systemic psoriasis treatments (e.g. fumarates), any investigational device or product (excluding psoriasis products); photochemotherapy (e.g. PUVA); granulocytes and monocytes adsorptive apharesis |
| 7 days | Anakinra |
*No treatment initiation 1 week prior to randomisation: phototherapy (e.g. UVA, UVB), topical treatment for psoriasis or any other skin condition (e.g. topical corticosteroids, topical vitamin D analogues, tar, anthralin, topical retinoids); no treatment initiation 2 weeks prior to randomisation, no dose escalation within 2 weeks prior to randomisation, and had to be discontinued prior to receiving the first dose: methotrexate, cyclosporine, retinoids.
† No restriction on inhaled corticosteroids to treat asthma or corticosteroid drops administered in the eye or ear.
AGEP=acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis; CRP=C-reactive protein; ERASPEN=European Rare and Severe Psoriasis Expert Network; GPP=Generalised Pustular Psoriasis; IL-36R=interleukin-36 receptor; IL-36RN=interleukin-36 receptor antagonist; PUVA=psoralen ultraviolet A; SAPHO=synovitis-acne-pustulosis-hyperostosis-osteitis; ULN=upper limit of normal; UVA=ultraviolet A; UVB=ultraviolet B.
EffisayilTM 1 study: baseline characteristics1,2
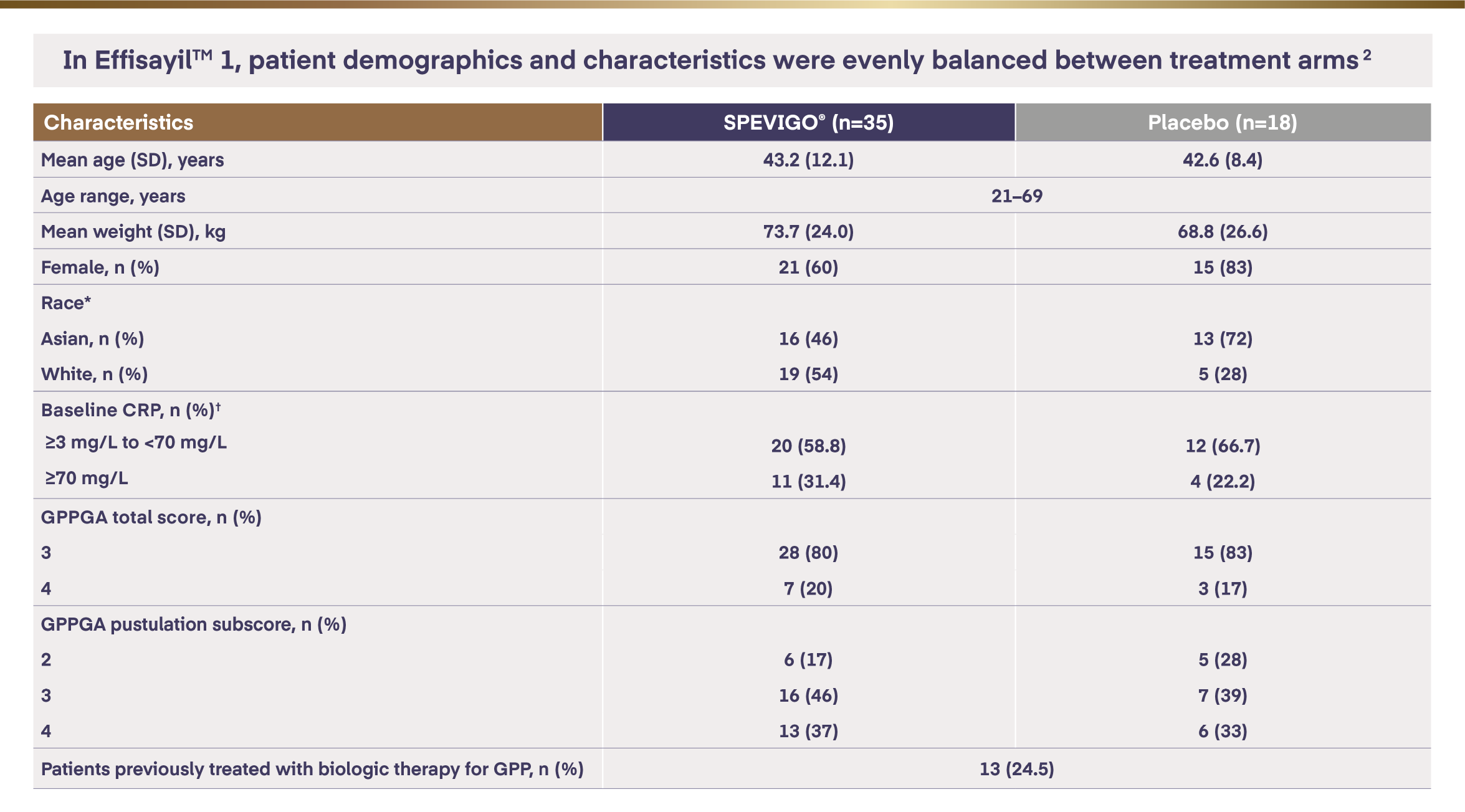
*Race was reported by the patient.
†A total of 52 patients were included; 5 patients had missing values at baseline.
CRP=C-reactive protein; GPPGA=Generalised Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment; SD=standard deviation.
The Generalised Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment (GPPGA) is used to evaluate flare symptoms and treatment efficacy3
The GPPGA score is adapted from the Physician Global Assessment, a tool physicians use to assess psoriatic lesions. The GPPGA is used to assess the severity of pustules, scaling, and erythema, using a 5-point scale ranging from 0 to 4, with higher score indicating greater disease severity.
To determine a patient’s GPPGA total score:

Step 1
Examine and assess the severity of pustules, erythema, and scaling

Step 2
Apply a score to each individual component

Step 3
Calculate the average to determine the total score
The GPPGA total score is determined by average subscores of pustules, erythema, and scaling. The components are graded separately. The average is calculated and the GPPGA total score is determined from the average composite score of erythema, pustules, and scaling: 0 (0 for all 3 components), 1 (average is >0 to <1.5), 2 (average is 1.5 to <2.5), 3 (average is 2.5 to <3.5), or 4 (average is: ≥3.5). To receive a score of 0 or 1, the patient must also be afebrile.
The GPPGA total score is the calculated average of the composite scores of pustules, erythema, and scaling skin6
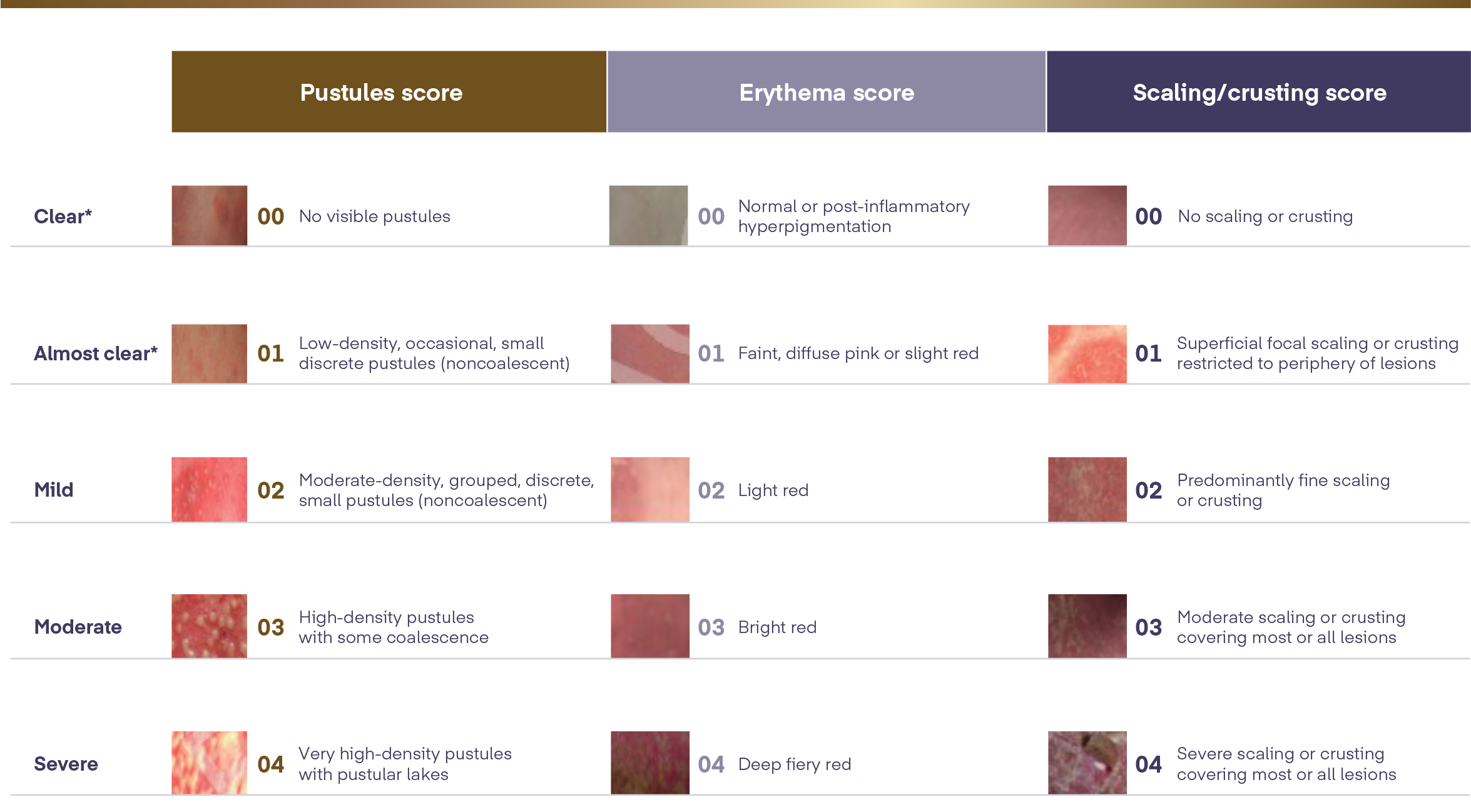
*To receive a score of 0 or 1, the patient should be afebrile, in addition to skin presentation requirements.6
GPPGA=Generalised Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment.
References
- SPEVIGO® Summary of Product Characteristics. Boehringer Ingelheim.
- Bachelez H, Choon SE, Marrakchi S, et al; for the Effisayil 1 Trial Investigators. Trial of spesolimab for generalised pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(26):2431-2440.
- Choon SE, Lebwohl MG, Marrakchi S, et al. Study protocol of the global Effisayil 1 phase II, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of spesolimab in patients with generalised pustular psoriasis presenting with an acute flare. BMJ Open. 2021;11(3):e043666.
- Navarini AA, Burden AD, Capon F, et al; for the ERASPEN Network. European consensus statement on phenotypes of pustular psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31(11):1792-1799.
- Choon SW, van de Kerkhof P, Gudjonsson JE, et al. International Consensus Definition and Diagnostic Criteria for Generalized Pustular Psoriasis from the International Psoriasis Council. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;160(7):758-768.
PC-GB-109365 V2 | March 2025

