Spevigo (spesolimab) has a conditional marketing authorisation for the treatment of generalised pustular psoriasis (GPP) flares in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age as monotherapy
▼This medicinal product is subject to additional monitoring. * Additional efficacy and safety data are being collected.
Click here for prescribing information.
SPEVIGO®▼ (spesolimab) safety information as per SmPC1
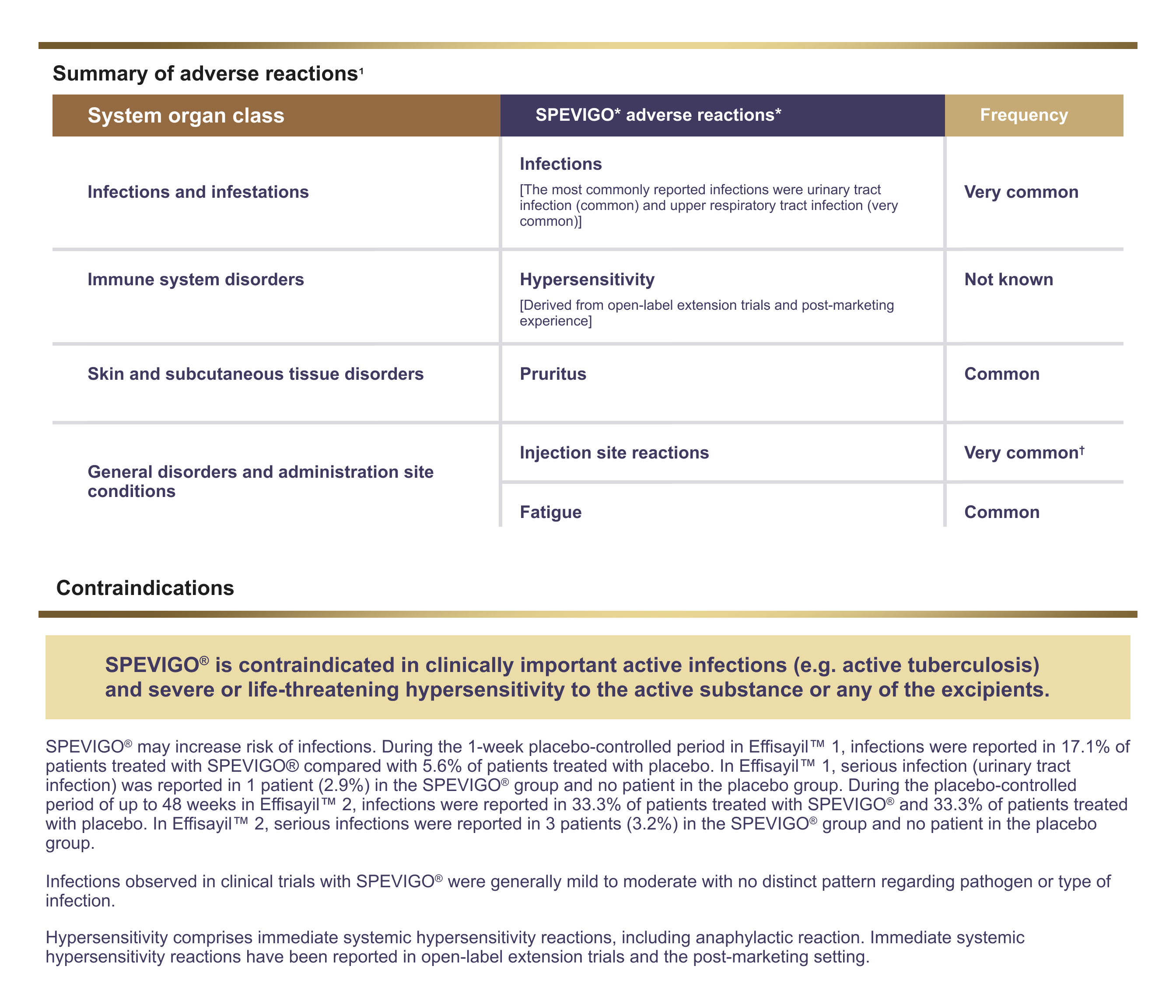
*The adverse reactions are listed by MedDRA System Organ Class (SOC) and frequency category using the following convention: very common (≥ 1/10), common (≥ 1/100 to < 1/10).
†Not reported in Effisayil™ 1.
MedDRA=Medical Dictionary for Drug Regulatory Activities; SmPC=Summary of Product Characteristics.
SPEVIGO® safety information as per Effisayil™ 1 trial2
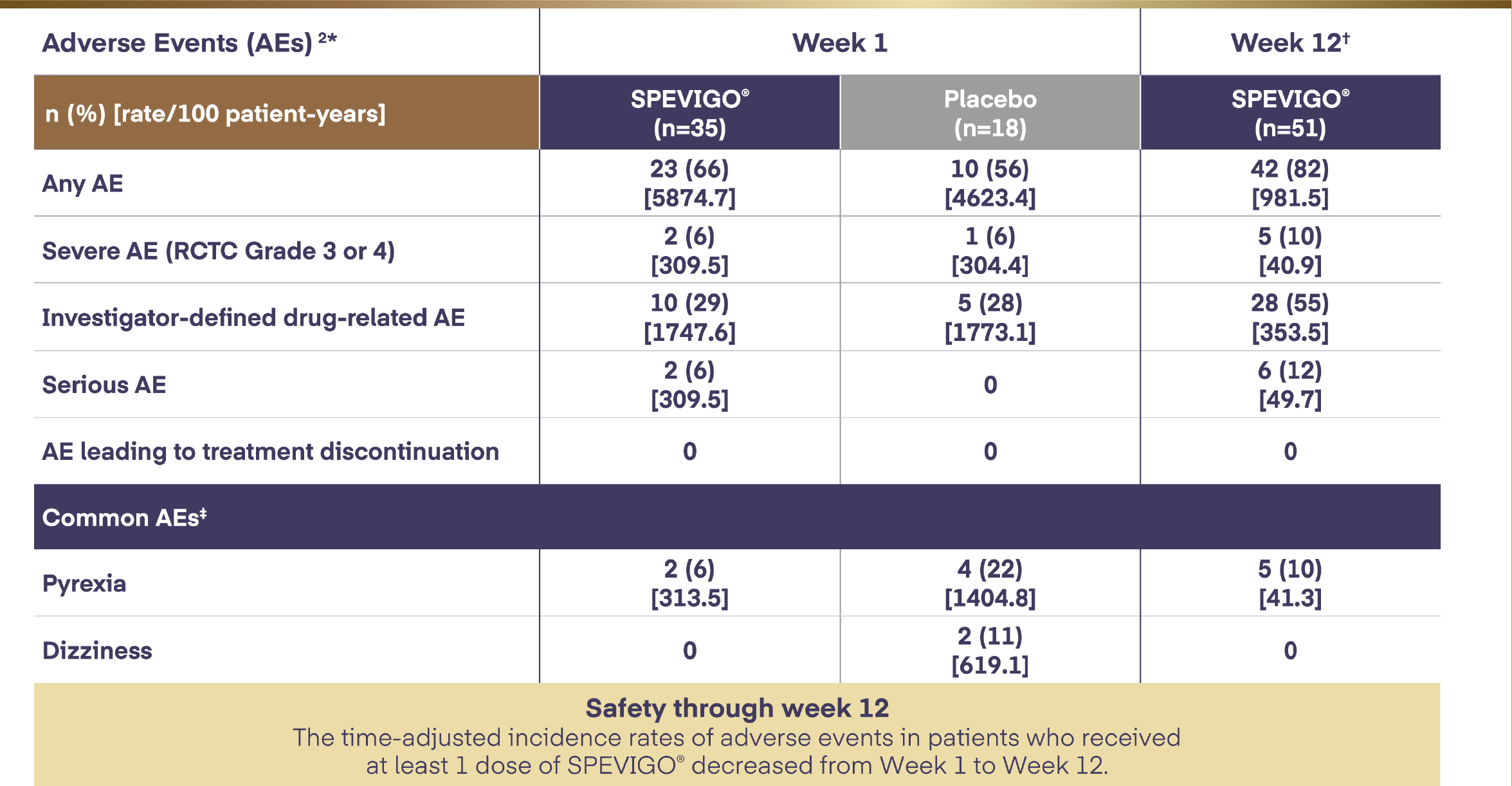
*All AEs occurring between the start of treatment and the end of the residual effect period (16 weeks after the placebo dose of SPEVIGO®) were coded using the Medical Dictionary for Drug Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) v23.1. AE severity was graded according to the RCTC v2.0. Pustular psoriasis was excluded as an AE from this safety analysis.
†Data set at Week 12 included patients randomised to SPEVIGO® who received up to 3 doses of SPEVIGO® and patients randomised to the placebo group who received OL SPEVIGO® at or after Day 8. All AEs in the residual effect period are included but censored at the day rescue treatment with SPEVIGO® was administered.
‡Common AEs are reported in ≥10% of patients in any treatment group.
AE=adverse event; OL=open-label; RCTC=Rheumatology Common Toxicity Criteria.
Special warnings and precautions for use1
Infections
SPEVIGO® may increase the risk of infections.
In patients with a chronic infection or a history of recurrent infection, the potential risks and expected clinical benefits of treatment should be considered prior to prescribing SPEVIGO®. Treatment with SPEVIGO® should not be initiated in patients with any clinically important active infection until the infection resolves or is adequately treated. Patients should be instructed to seek medical advice if signs or symptoms of clinically important infection occur after treatment with SPEVIGO®.
Pre-treatment evaluation for tuberculosis
Prior to initiating treatment with SPEVIGO®, patients should be evaluated for tuberculosis (TB) infection. SPEVIGO® is contraindicated to patients with active TB infection.
Anti-TB therapy should be considered prior to initiating SPEVIGO® treatment in patients with latent TB, a history of TB or possible previous exposure to people with active TB in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed. After SPEVIGO® treatment, patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of active TB.
Hypersensitivity and infusion-related reactions
Hypersensitivity and infusion-related reactions may occur with monoclonal antibodies such as spesolimab (SPEVIGO®). Hypersensitivity may include immediate reactions such as anaphylaxis and delayed reactions such as drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
If a patient develops signs of anaphylaxis or other serious hypersensitivity, SPEVIGO® treatment should be discontinued immediately and appropriate treatment should be initiated.
Immediate hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic reactions have been reported in patients treated with spesolimab.
If a patient develops mild or moderate hypersensitivity during an intravenous infusion or other infusion-related reactions, treatment should be stopped and appropriate medical therapy should be considered (e.g., systemic anti-histamines and/or corticosteroids). Upon resolution of the reaction, the infusion may be restarted at a slower infusion rate with gradual increase to complete the infusion.
Use in patients with an immediate, life-threatening GPP flare
There is no experience from the use of SPEVIGO® in patients with an immediate, life-threatening flare of GPP or a flare requiring intensive care treatment.
Concomitant use with other GPP treatments
The safety and efficacy of SPEVIGO® in combination with immunosuppressants, including biologics, have not been evaluated systematically. In the GPP flare treatment clinical study, there was a washout period for most other treatments (biologics, other systemic immunomodulating treatments), while some treatments were discontinued before initiation of SPEVIGO® treatment with no washout period required (methotrexate, ciclosporin, retinoids, topical treatments).
Concomitant use of other immunosuppressants and SPEVIGO® is not recommended. At initiation of SPEVIGO® treatment, other GPP treatments should be stopped and other treatments (e.g. with systemic immunosuppressants) should not be used concomitantly to treat the flare.
Re-treatment
Very limited efficacy and safety data are available for re-treatment with SPEVIGO® for a subsequent new flare. In Effisayil™ 1, five patients received re-treatment for a subsequent new flare and were followed up for a minimum of 8 weeks.
Immunisations
It is unknown whether SPEVIGO® affects the efficacy of vaccines.
No data are available on the potential secondary transmission of infection by live vaccines in patients receiving SPEVIGO®. The interval between live vaccinations and initiation of SPEVIGO® therapy should be at least 4 weeks. Live vaccines should not be administered for at least 16 weeks after treatment with SPEVIGO®.
Peripheral neuropathy
The potential for peripheral neuropathy with SPEVIGO® is unknown. Cases of peripheral neuropathy have been reported in clinical trials with SPEVIGO®. Physicians should be vigilant for symptoms potentially indicative of new-onset peripheral neuropathy.
Traceability
In order to improve the traceability of biological medicinal products, the name and the batch number of the administered product should be clearly recorded.
Excipients
This medicinal product contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per dose, that is to say essentially ‘sodium free’.
GPP=Generalised Pustular Psoriasis; TB=Tuberculosis; DRESS=drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms.
Pregnancy, fertility, lactation, paediatric population and storage precautions1
Pregnancy
There are no or limited data from the use of SPEVIGO® in pregnant women. Non-clinical studies using a surrogate, mouse specific anti-IL-36R monoclonal antibody do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to reproductive toxicity. Human immunoglobulin (IgG) is known to cross the placental barrier. As a precautionary measure, it is preferable to avoid the use of SPEVIGO® during pregnancy.
Fertility
There are no data available on the effect of SPEVIGO® on human fertility. Studies in mice using a surrogate, mouse specific anti-IL-36R monoclonal antibody, do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to fertility from antagonism of IL-36R.
Breast-feeding
No data are present on excretion of SPEVIGO® in human milk. In humans, excretion of IgG antibodies in milk occurs during the first few days after birth, which is decreasing to low concentrations soon afterwards. Consequently, transfer of IgG antibodies to the newborns through milk, may happen during the first few days. In this short period, a risk to the breastfed child cannot be excluded. Afterwards, SPEVIGO® can be used during breastfeeding if clinically needed. If treatment was discontinued before the last trimester of pregnancy, breastfeeding can be started immediately after birth.
Paediatric population
The safety and efficacy of SPEVIGO® in children less than 12 years of age has not been established. No data are available.
References
- SPEVIGO® Summary of Product Characteristics. Boehringer Ingelheim.
- Bachelez H, Choon SE, Marrakchi S, et al; for the Effisayil 1 trial investigators. Trial of spesolimab for generalised pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(26):2431-2440.
PC-GB-109367 V3 | July 2025

