Making the Case for Action: Addressing Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
The Hidden Burden of CKD1
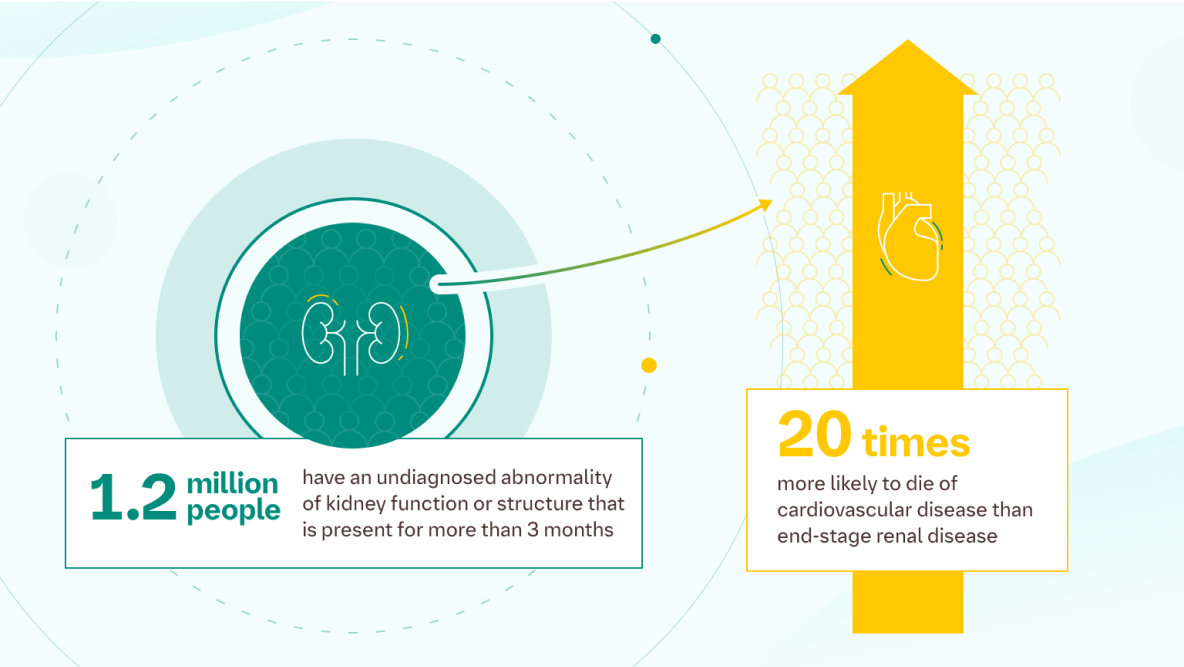
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a long-term abnormality of kidney function or structure that persists for more than three months. Despite its significant health implications, an estimated 1.2 million people in England remain undiagnosed, making early detection a critical challenge.
The Link Between CKD and Cardiovascular Disease
One of the most concerning aspects of CKD is its strong association with cardiovascular disease (CVD). Patients with CKD are 20 times more likely to die from cardiovascular disease than from end-stage renal disease (ESRD). This highlights the urgent need for early diagnosis and proactive management to prevent serious complications.
1 of 3. What is the Burden of CKD and How Does Dialysis Affect It?
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a progressive disease and acts as a CV risk multiplier2
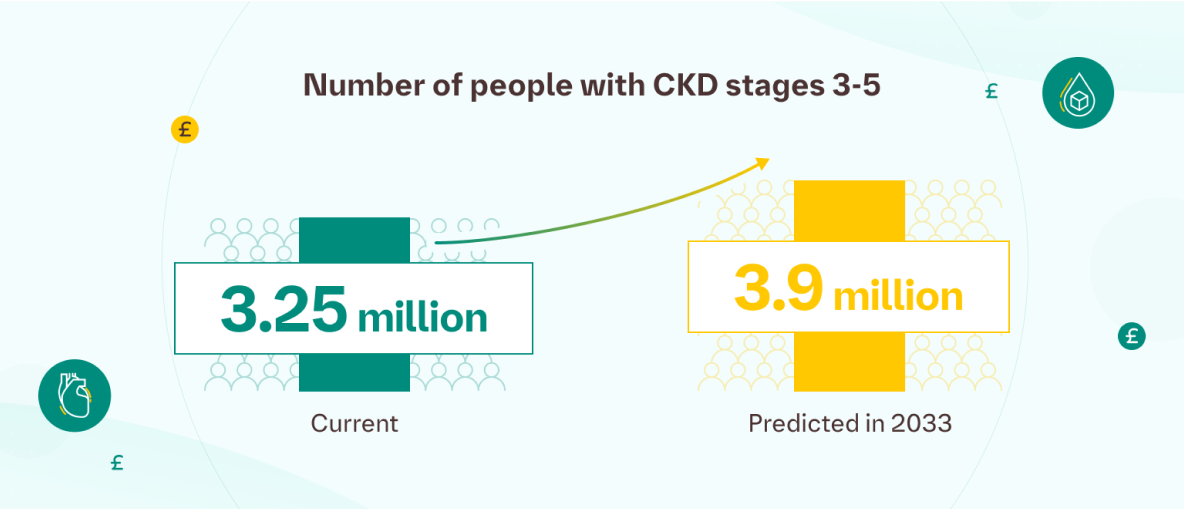
- 3.25 million people in the UK currently live with CKD stages 3-5.3
- 3.9 million people are estimated to have CKD stages 1-2.3
- By 2033, CKD stages 3-5 cases are expected to rise to 3.9 million.3
This increase is largely due to an ageing population and the prevalence of risk factors such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and the impact of health and economic inequalities.3
Dialysis is a significant contributor to the economic impact of kidney disease.
- The estimated annual cost is £34,000 per patient (2023) – over three times the annual state pension.3
- The total yearly economic burden of kidney disease in the UK is £7 billion.3
- Of this, £6.4 billion represents direct costs to the NHS.3
- Kidney disease accounts for approximately 3.2% of the NHS budget.3
Dialysis funding will be moving from central to local budgets, as of 2025. Have you thought about how this may affect your primary care practice?
How Can You Manage the Burden of CKD?
Emerging evidence suggests that the impact of CKD can be mitigated through strategies such as early detection, appropriate pharmacological treatment, and proactive outreach initiatives.3
A number of interventions have been cited as having the potential to improve clinical outcomes for those affected by CKD.3




2 of 3. How Prevalent is CKD in Your Patient Population?
This interactive dashboard is based on NHS England QOF data, allowing you to explore diagnosed CKD prevalence across England by Integrated Care Board (ICB), primary care network, or individual practice.
Explore data across England, filtered by Integrated Care Board (ICB), primary care network or individual practices, and empower your decision-making with evidence-based insights to identify where JARDIANCE® may be able to aid patient care.
-
*
Estimated patients over the age of 18, with CKD stages 3-5.2
-
†
Estimated patients over the age of 18, with CKD stages 3-5 excluding stage 5.4
-
‡
Estimated eligible adult CKD patients with CKD stage 3-4, that are on an ACE/ARB, but not on an SGLT2i.2,4,5
Notes
CKD Patients in QOF include those with T2D.
SGLT2i patients driven from NHS Prescribing.
Assumptions
2.5% of CKD patients Stages 3-5 are on Stage 5 (IQVIA LPD).
Of all SGLT2i Patients, 25.5% have CKD. Of those, 75.5% are in stages 3-4 (IQVIA LPD).
Of all CKD patients in Stages 3-4 that are not on an SGLT2i, 42.1% of them are on an ACE or an ARB (IQVIA LPD).
3 of 3. How Could SGLT2 Inhibitors Help in Managing CKD?
Based on Kidney Research UK epidemiological and health-economic modelling, timely use of SGLT2 inhibitors is projected to delay CKD progression and reduce the risk of dialysis and hospitalisation vs placebo.3

Slows CKD progression and reduces end-stage kidney disease in eligible patients vs placebo.*

Fewer patients progress to dialysis with timely use of SGLT2 inhibitors vs placebo.†

Reduces hospitalisations linked to CKD and cardiovascular complications vs placebo.‡
-
*
SGLT2 inhibitors significantly delay CKD progression and the incidence of ESKD in patients with or without diabetes.3
-
†
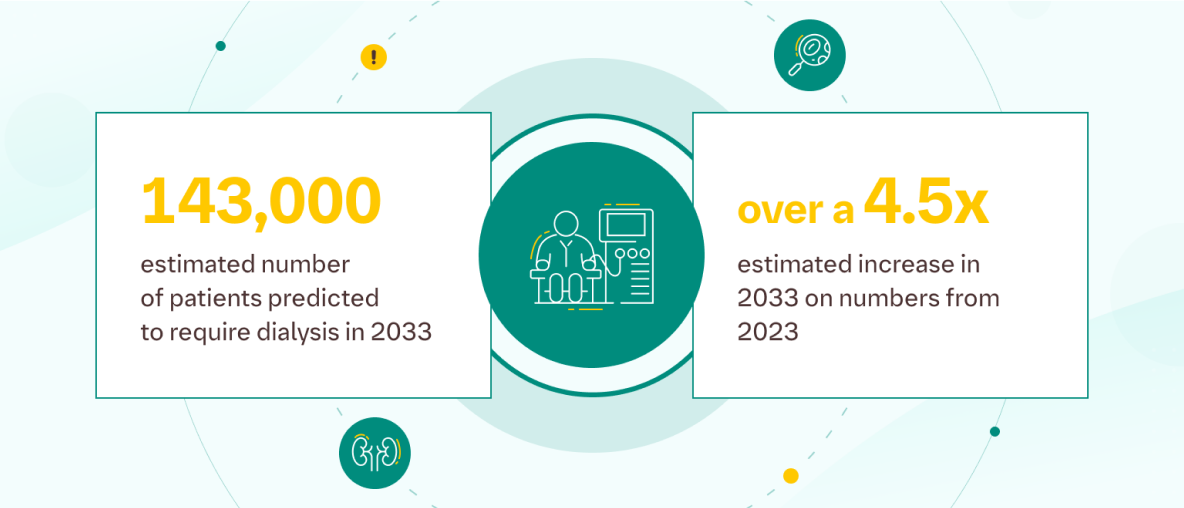
Modelling suggests the increased use of SGLT2 inhibitors could result in 1,960 fewer patients needing dialysis over a 10-year period.3
-
‡
Economic modelling suggests reduced hospitalisation leads to an estimated cost saving of £70.9 million over 10 years.3
-
-
*
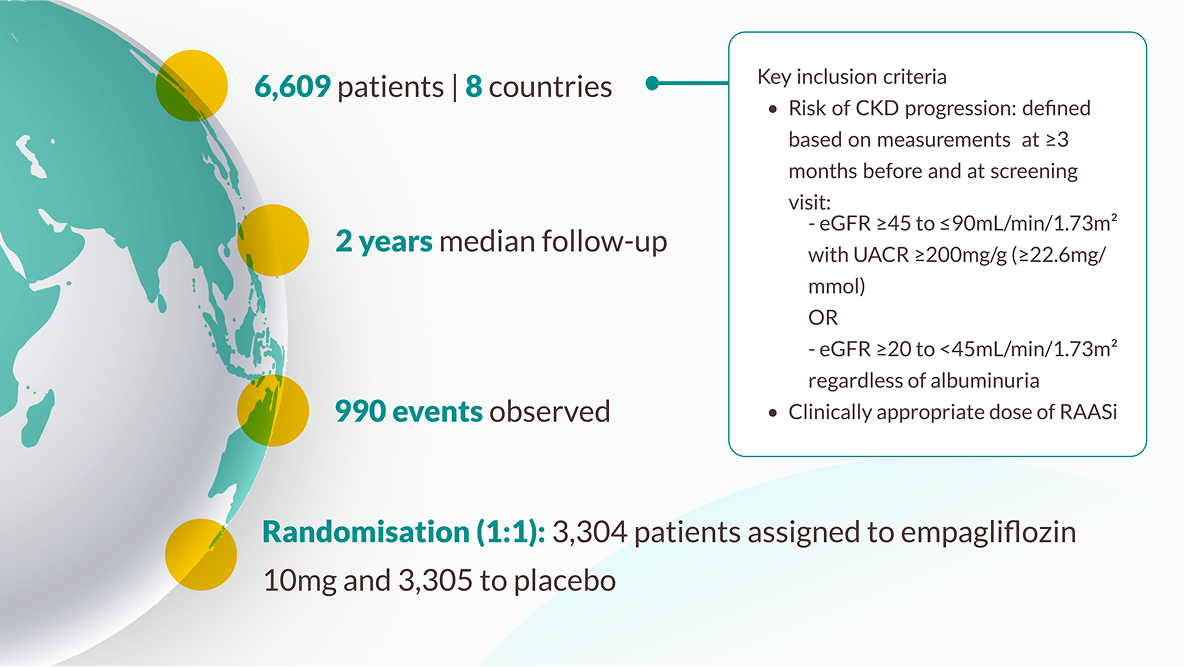
The trial enrolled 6,609 patients who had evidence of CKD at risk of kidney disease progression, with and without diabetes, with and without albuminuria. Patients with an eGFR ≥20 to <45 mL/min/1.73m2 , or an eGFR ≥45 to <90 mL/ min/1.73m2 with a UACR ≥200mg/g, were randomised to receive either 10mg empagliflozin (n=3304) or placebo (n=3305) on top of standard of care. JARDIANCE® achieved primary endpoint vs placebo: risk reduction in kidney disease progression or CV death 28% RRR/3.6% ARR (HR=0.72; 95% CI: 0.64, 0.82; p<0.001). Kidney disease progression was defined as end stage kidney disease (ESKD: the initiation of maintenance dialysis or receipt of a kidney transplant), a sustained decrease in the eGFR to <10 mL/min/1.73m2 , a sustained decrease from baseline in the eGFR of at least 40%, or death from renal causes. 10,11
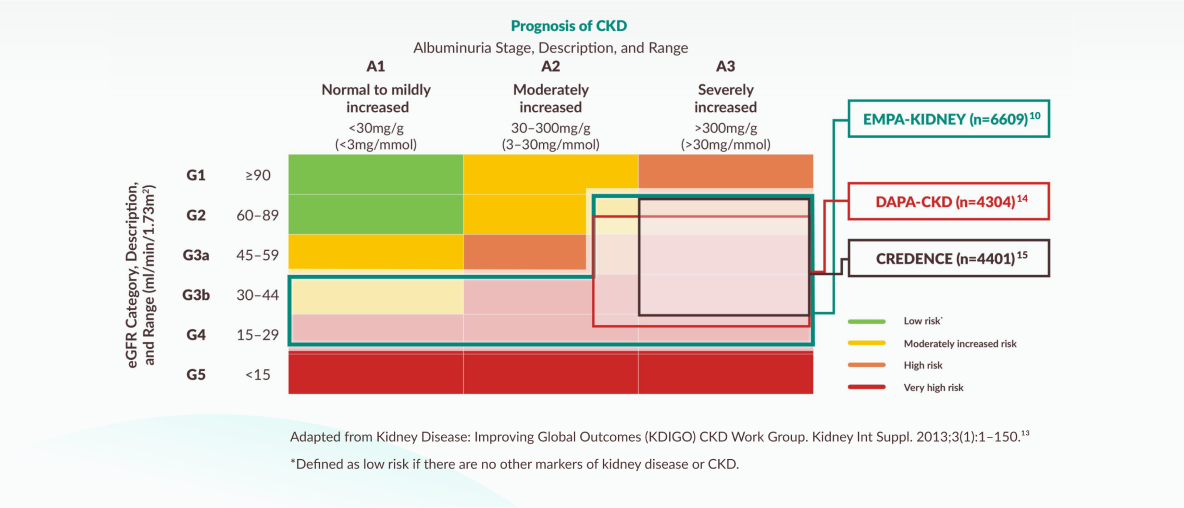
EMPA KIDNEY included the broadest range of patients amongst the SGLT2i CKD RCTs in terms of eGFR and those with and without albuminuria10,14,15
Inclusion criteria of the SGLT2i CKD trials mapped to KDIGO guidance
NICE 2023 TA942 recommendation for the use of empagliflozin in adults with CKD when mapped to the KDIGO 2024 guidance on CKD prognosis by eGFR and albuminuria categories. It is recommended as an add on to optimised standard care including the highest tolerated licensed dose of ACE inhibitors or ARBs, unless these are contraindicated.16
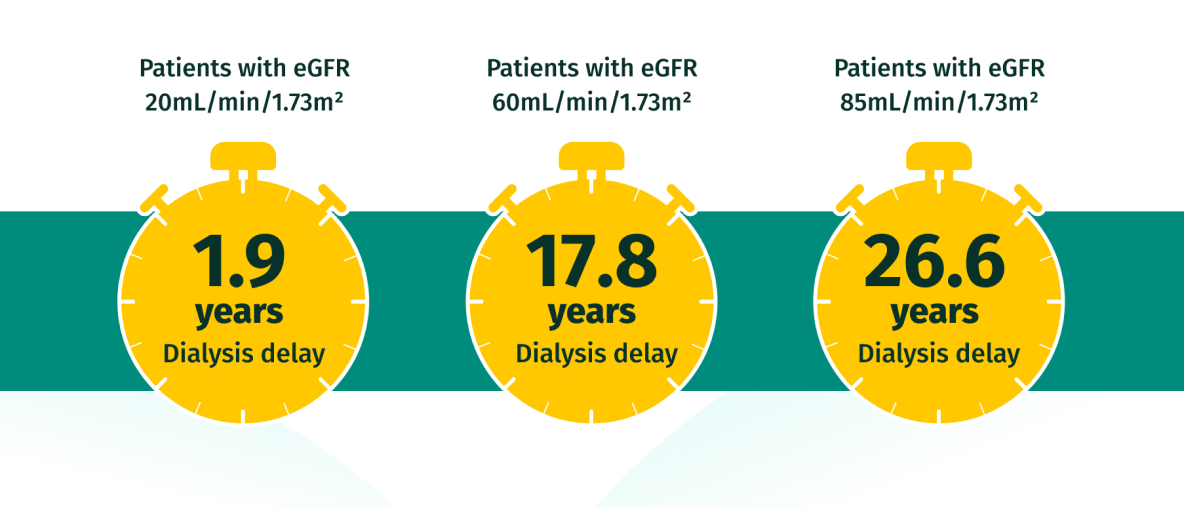
EARLY intervention with JARDIANCE may help patients avoid dialysis for longer17
Potential impact on time to dialysis versus SoC based on extrapolated data from the EMPA-KIDNEY trial
Based on hypothetical transformation of chronic eGFR slopes into time to kidney failure, i.e., time to need for kidney replacement therapy, defined as eGFR = 10mL/min/1.73m2. Data estimated from each baseline eGFR value by applying the chronic eGFR slopes corresponding to participants on standard of care vs empagliflozin within the prespecified eGFR subgroups (eGFR cutoff points to define subgroups).

Identify patients who could benefit from JARDIANCE®

JARDIANCE® CKD patient booklet

JARDIANCE® Initiation & Management guide for T2D, CHF and CKD
Abbreviations
Px: Patient; Rx: Prescription / Treatment; LPD: Latest Prescribing Data; RCT: Randomised Controlled Trial.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). CVD prevention: chronic kidney disease detection and management. Available from https://stpsupport.nice.org.uk/cvd-prevention-ckd/index.html (Accessed April 2025).
- NHS England. Quality and Outcomes Framework, 2023-2024. Available from https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/quality-and-outcomes-framework-achievement-prevalence-and-exceptions-data/2023-24 (Accessed April 2025).
- Kidney Research UK: A UK public health emergency. The health economic of kidney disease to 2033. June 2023. Available at: https://www.kidneyresearchuk.org/about-us/influencing-change/health-economics-report/ (Accessed April 2025).
- IQVIA LPD, Ad-hoc Report [BI_HF_REGT_ADH.DN2] , Standard Panel, MAT November 2024, (Accessed April 2025).
- OpenPrescribing. Available at https://openprescribing.net/analyse/ (Accessed April 2025).
- Zinman B, et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(22):2117–2128.
- Claggett B, et al. Circulation. 2018;138:1599–1601.
- Verma S et al. ESC Heart Fail. 2021;8(4):2603–2607.
- JARDIANCE (empagliflozin) Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC).
- Herrington WG, et al. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(2):117-127. (EMPA-KIDNEY results and the publication’s Supplementary Appendix).
- JARDIANCE Data on File (EMP 23-22).
- JARDIANCE Data on File (EMP 23-13).
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. Kidney Int.2024;105(4S):S117-S314.
- Heerspink HJL et al. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1436–1446.
- Perkovic V et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2295–2306.
- NICE. Empagliflozin for treating chronic kidney disease: Technology appraisal guidance (TA942). 2023. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta942/.
- Fernández-Fernandez B, Sarafidis P, Soler MJ, Ortiz A. Clin Kidney J. 2023;16(8):1187–1198.
PC-GB-109987 | July 2025
The content on this website is in relation to adult patients.
Empagliflozin is not recommended in severe hepatic impairment, breastfeeding, Type 1 diabetes and is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to the active ingredient or any of its excipients. Empagliflozin should be avoided in pregnancy.
Please consult the SmPC for full details regarding adverse events, monitoring requirements and interactions prior to prescribing JARDIANCE®.
- JARDIANCE® (empagliflozin) UK Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC). Available at:
http://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/28973.
JARDIANCE® is indicated for the treatment of adults with insufficiently controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus as an adjunct to diet and exercise
- as monotherapy when metformin is considered inappropriate due to intolerance
- in addition to other medicinal products for the treatment of diabetes1
JARDIANCE® is indicated in adults for the treatment of chronic kidney disease.1
JARDIANCE® is indicated in adults for the treatment of symptomatic chronic heart failure.1
PC-GB-109995 V4 | October 2025